What are Broken Rotor bar Faults?!
Induction machines are one of the crucial elements of many industrial processes nowadays (IM). These machines are prone to rotor, stator, or bearing failure due to diverse operating circumstances. All of these IM flaws have the potential to impair output, harm neighboring equipment, or, in the worst case, lead to the system’s complete failure[1]–[3].
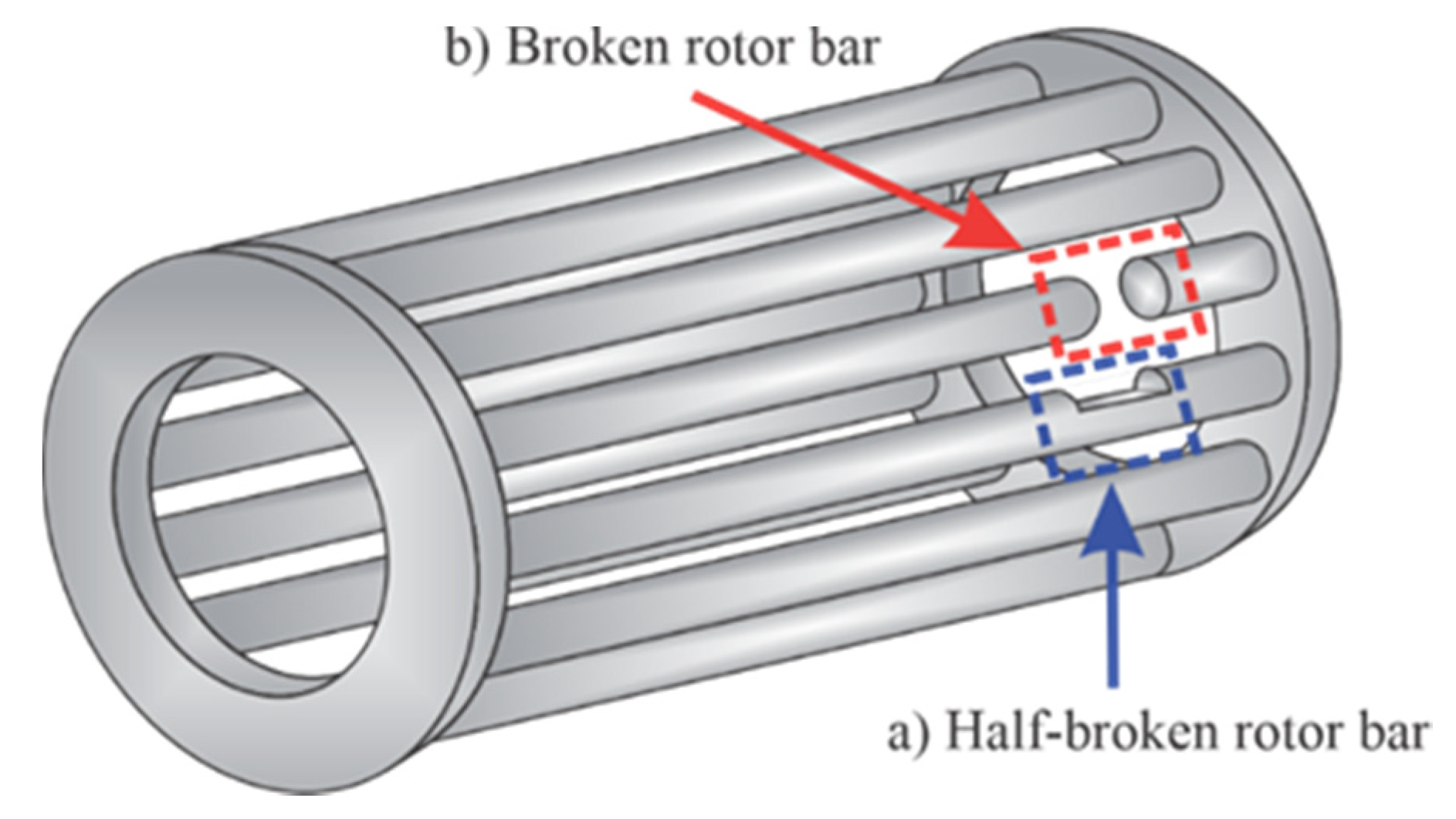
Induction machines have been in use since the early 1800s. The operators or the equipment close to the working zones may be at danger from this motor’s strong starting torque and high operating speeds. Broken rotor bar defects are one of the frequent causes of motor failure, which may also be brought on by an unfavorable operating environment or artificial mis-operation during the manufacturing process. The rotor bar will first fracture locally, and the surrounding area will experience increased stress. As the defect worsens, the rotor bar entirely breaks, along with any adjacent bars, and finally the whole motor collapses. The early detection of a damaged rotor bar is thus essential to reduce financial losses and prepare for regular maintenance.
[1] E. R. Ferrucho-Alvarez, A. L. Martinez-Herrera, E. Cabal-Yepez, C. Rodriguez-Donate, M. Lopez-Ramirez, and R. I. Mata-Chavez, “Broken rotor bar detection in induction motors through contrast estimation,” Sensors, vol. 21, no. 22, Nov. 2021, doi: 10.3390/s21227446.
[2] IEEE EUROCON 2019 -18th International Conference on Smart Technologies. IEEE, 2019.
[3] C. Pezzani, P. Donolo, G. Bossio, M. Donolo, A. Guzman, and S. E. Zocholl, “Detecting broken rotor bars with zero-setting protection,” IEEE Trans Ind Appl, vol. 50, no. 2, pp. 1373–1384, 2014, doi: 10.1109/TIA.2013.2276116.
Comments
Post a Comment